About Us
Simplifying Fluid Dynamics for accurate modelling in over-pumping applications.
Pump selection by matching performance curves and pump specifics to your application
The most theoretically correct equation is the Darcy-Weisbach equation.
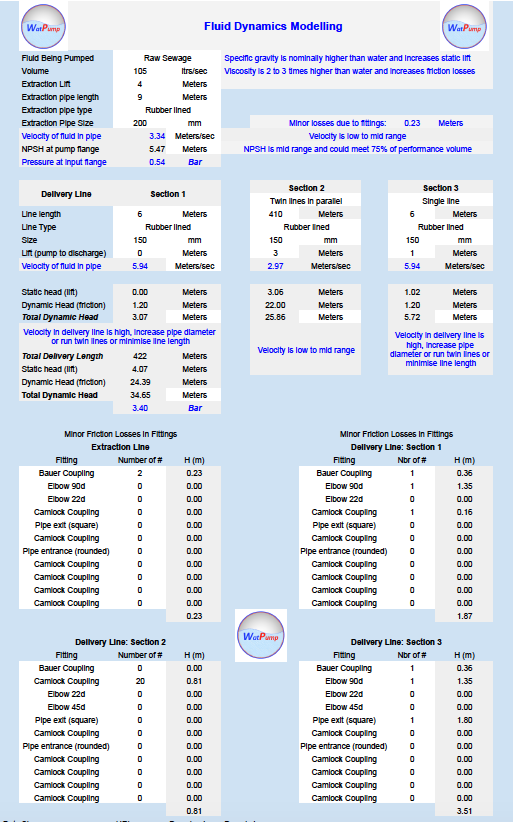
Simplified data inputs
Drop down boxes guide key data inputs Optional SI, Imperial or US units for input and results; Minor loss factors also available for complete calculations
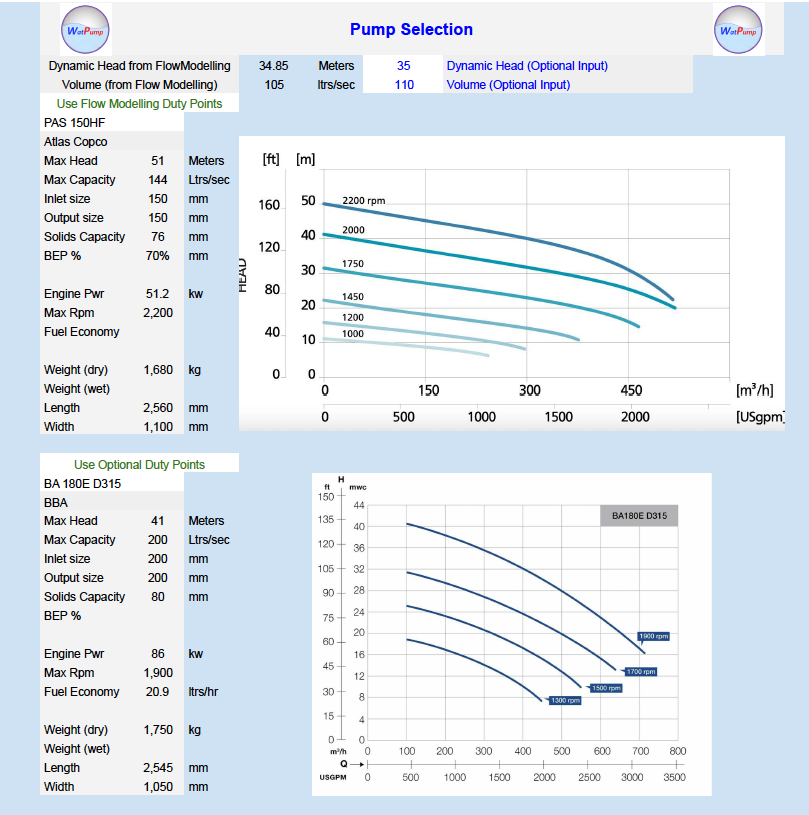
Pump selection shortlists
Pumps can be selected from a drop down box of possible and probable pumps.
Pump selection can be run from the Fluid Dynamics calculated duty point or alternately by your own manually inputed duty point in the 'Pump Selection' form.
Selected pumps provide a full performance curve and key operational data.
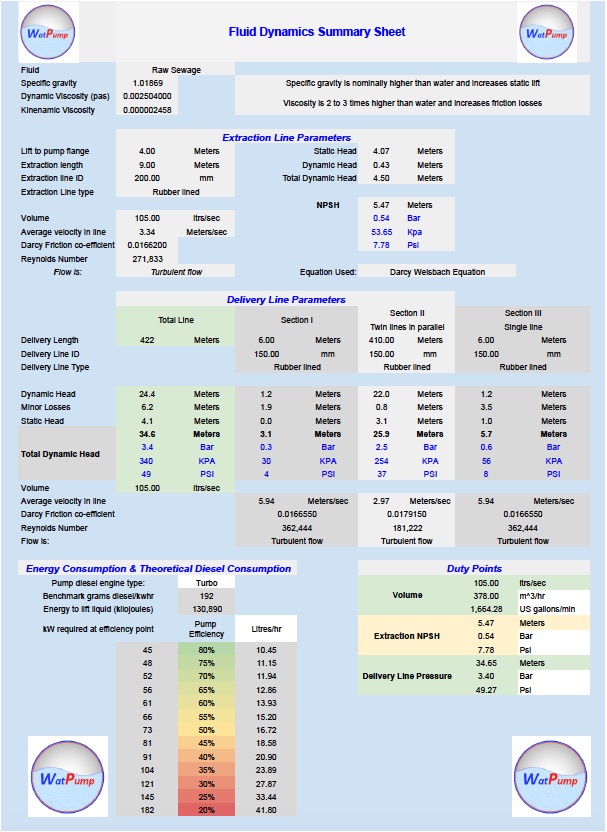
Summary Certificate
A job summary certificate provides a full data sheet including Reynolds number, Darcy-Weisbach friction coefficient, flow status, major losses, minor losses, energy consumption with indicative fuel burn based on pump efficiency
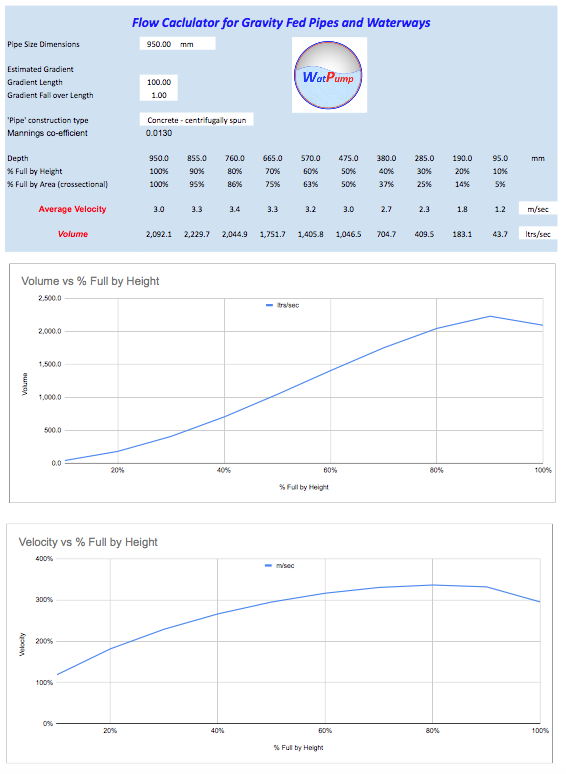
How much flow.................
Flow Calculator for Gravity fed pipes and waterways........
Manning first proposed his formula to the Institution of Civil Engineers (Ireland) in 1889 at the age of 73. It is an empirical equation (based on observed outcomes) and is widely accepted for open waterways and gravity fed pipes. In many practical applications engineers are unable to provide expected flows through pipelines for over-pumping proposals, the Mannings formulae provides expected flow rates from low partial-fill through to full pipe capacity.

